Diesel engines are renowned for their high efficiency, torque, and longevity. However, they also produce excessive exhaust gas emissions, particularly in terms of carbon soot particles and NOx. To comply with increasingly stringent emissions regulations, certain internal measures can be taken to minimize emissions outside the engine. Additionally, external controls are now required to meet these regulations.
The most common emissions control systems used in diesel engines include diesel particulate filters (DPF), urea-SCR catalysts, NOx adsorbers, and EGR valves. The EGR valve is the component responsible for controlling the flow of exhaust gases destined to re-enter the intake stream. There are two types of EGR valves: on the cold side and on the hot side. The type of activation varies from pneumatic to hydraulic and electric (the latter being the most common today).
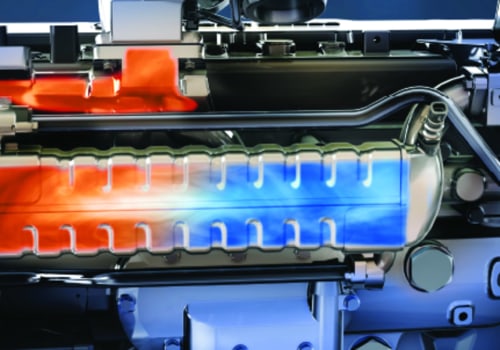
The EGR valves on the cold side direct exhaust gases to the intake after they have left the EGR coolers. An EGR valve on the hot side performs its flow functions before EGR coolers. This helps reduce the accumulation of soot and dirt that causes valve failure when exhaust gas temperatures exceed 1200 degrees F in most engine applications. The task of lowering these temperatures is performed by the EGR cooler, an air-liquid heat exchanger that uses the engine's circulated coolant to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases that pass through it.
The diesel particulate filter collects soot which periodically triggers a regeneration cycle. This cycle consists of a combination of diesel fuel and exhaust gases inside the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) that transforms soot into fine ash. Miller's modification of the diesel engine is another means of reducing NOx and is believed to be used by Caterpillar for its ACERT diesel. The disadvantage of SCR is the greater complexity of the diesel exhaust gas aftertreatment system and the fact that DEF freezes before diesel fuel.
The diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) is another exhaust gas aftertreatment that is standard today for highway diesel engines, and is placed just in front of the DPF can.