The Diesel Technology Forum has stated that there is no cost-effective alternative to diesel engines when it comes to efficiently feeding the world's crops. Diesel-powered equipment is an integral part of the supply chain that transports food from farm to table, and it powers more than two-thirds of all agricultural equipment, moves 90% of its product, and pumps one-fifth of the water in the United States. The agricultural and trucking industries are trying to comprehend the implications of this order, as well as the many challenges that lie ahead. Urban areas have already started investing in charging stations for electric cars, but this infrastructure is not available in rural areas where farmers and ranchers work.
The electric diesel starter was used in low-compression diesel engines by connecting two 6-volt batteries in series to get 12 volts only for the starter, but leaving them in parallel for the lights and charging. Not only are diesel fuel and clean-tech diesel engines making American agriculture more productive and economically significant, but they are also working behind the scenes to conserve fuel, save money, and reduce harmful gases that contribute to pollution from this sector. Diesel has an advantage from the start since it has more calorific value than gasoline. When Caterpillar delivered its new 60 diesel caterpillar for testing at the University of Nebraska tractor testing center on June 14, 1932, it was so hard to find diesel fuel that the No.
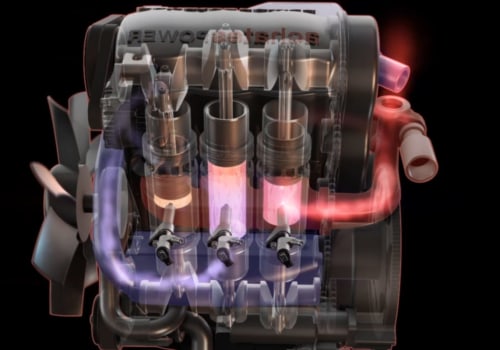
Compliance with these stringent “Level 4” US emission standards is achievable thanks to the use of ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel, high-tech diesel engines, emission control systems, and subsequent exhaust gas treatment.